Coordinating a large quantity of information in Microsoft Excel is a time-consuming headache. Fortunately, you do not have to. The VLOOKUP operate might help you automate this activity and prevent tons of time.

What does VLOOKUP do, precisely? This is the easy rationalization: The VLOOKUP operate searches for a particular worth in your knowledge, and as soon as it identifies that worth, it may discover — and show — another piece of data that is related to that worth.
Microsoft Excel’s VLOOKUP operate is simpler to make use of than you assume. What’s extra, it’s extremely highly effective, and is unquestionably one thing you need to have in your arsenal of analytical weapons.
Skip to:
How does VLOOKUP work?
VLOOKUP stands for “vertical lookup.” In Excel, this implies the act of wanting up knowledge vertically throughout a spreadsheet, utilizing the spreadsheet’s columns — and a novel identifier inside these columns — as the idea of your search. If you search for your knowledge, it have to be listed vertically wherever that knowledge is positioned.
VLOOKUP Excel Method
Microsoft describes the VLOOKUP formulation or operate as follows:
=VLOOKUP(lookup worth, vary containing the lookup worth, the column quantity within the vary containing the return worth, Approximate match (TRUE) or Precise match (FALSE)).
It helps to arrange your knowledge in a manner in order that the worth you need to search for is to the left of the return worth you need to discover.
The formulation all the time searches to the suitable.
When conducting a VLOOKUP in Excel, you are primarily on the lookout for new knowledge in a distinct spreadsheet that’s related to outdated knowledge in your present one. When VLOOKUP runs this search, it all the time seems for the brand new knowledge to the proper of your present knowledge.
As an illustration, if one spreadsheet has a vertical listing of names, and one other spreadsheet has an unorganized listing of these names and their e mail addresses, you should use VLOOKUP to retrieve these e mail addresses within the order you’ve got them in your first spreadsheet. These e mail addresses have to be listed within the column to the suitable of the names within the second spreadsheet, or Excel will not have the ability to discover them. (Go determine … )
The formulation wants a novel identifier to retrieve knowledge.
The key to how VLOOKUP works? Distinctive identifiers.
A singular identifier is a bit of data that each of your knowledge sources share, and — as its title implies — it’s distinctive (i.e. the identifier is just related to one report in your database). Distinctive identifiers embrace product codes, stock-keeping models (SKUs), and buyer contacts.
Alright, sufficient rationalization: let’s examine one other instance of the VLOOKUP in motion!
VLOOKUP Excel Instance
Within the video beneath, we’ll present an instance in motion, utilizing the VLOOKUP operate to match e mail addresses (from a second knowledge supply) to their corresponding knowledge in a separate sheet.
Creator’s observe: There are numerous totally different variations of Excel, so what you see within the video above won’t all the time match up precisely with what you may see in your model. That is why we encourage you to comply with together with the written directions beneath.
Learn how to Use VLOOKUP in Excel
- Determine a column of cells you’d wish to fill with new knowledge.
- Choose ‘Perform’ (Fx) > VLOOKUP and insert this formulation into your highlighted cell.
- Enter the lookup worth for which you need to retrieve new knowledge.
- Enter the desk array of the spreadsheet the place your required knowledge is positioned.
- Enter the column variety of the info you need Excel to return.
- Enter your vary lookup to search out a precise or approximate match of your lookup worth.
- Click on ‘Achieved’ (or ‘Enter’) and fill your new column.
To your reference, here is what the syntax for a VLOOKUP operate seems like:
VLOOKUP(lookup_value , table_array , col_index_num , range_lookup)
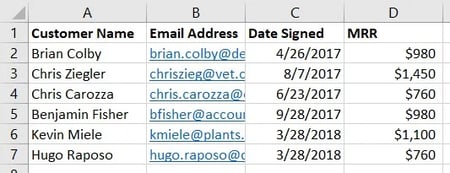
Within the steps beneath, we’ll assign the suitable worth to every of those parts, utilizing buyer names as our distinctive identifier to search out the MRR of every buyer.
1. Determine a column of cells you’d wish to fill with new knowledge.
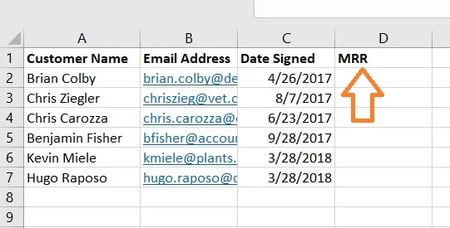
Bear in mind, you are trying to retrieve knowledge from one other sheet and deposit it into this one. With that in thoughts, label a column subsequent to the cells you need extra data on with a correct title within the prime cell, resembling “MRR,” for month-to-month recurring income. This new column is the place the info you are fetching will go.
2. Choose ‘Perform’ (Fx) > VLOOKUP and insert this formulation into your highlighted cell.
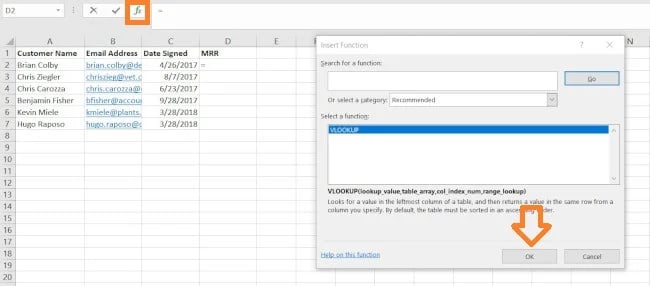
To the left of the textual content bar above your spreadsheet, you may see a small operate icon that appears like a script: Fx. Click on on the primary empty cell beneath your column title after which click on this operate icon. A field titled Method Builder or Insert Perform will seem to the suitable of your display screen (relying on which model of Excel you’ve got).
Seek for and choose “VLOOKUP” from the listing of choices included within the Method Builder. Then, choose OK or Insert Perform to start out constructing your VLOOKUP. The cell you presently have highlighted in your spreadsheet ought to now seem like this: “=VLOOKUP()“
You too can enter this formulation right into a name manually by getting into the daring textual content above precisely into your required cell.
With the =VLOOKUP textual content entered into your first cell, it is time to fill the formulation with 4 totally different standards. These standards will assist Excel slender down precisely the place the info you need is positioned and what to search for.
3. Enter the lookup worth for which you need to retrieve new knowledge.
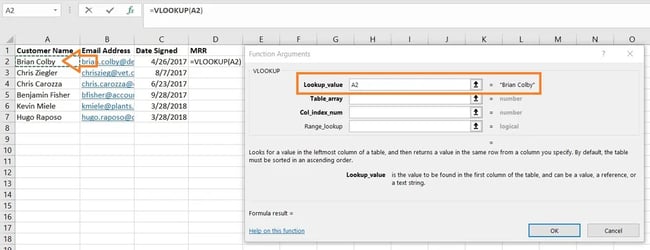
The primary standards is your lookup worth — that is the worth of your spreadsheet that has knowledge related to it, which you need Excel to search out and return for you. To enter it, click on on the cell that carries a price you are looking for a match for. In our instance, proven above, it is in cell A2. You may begin migrating your new knowledge into D2, since this cell represents the MRR of the client title listed in A2.
Take into accout your lookup worth might be something: textual content, numbers, web site hyperlinks, you title it. So long as the worth you are wanting up matches the worth within the referring spreadsheet — which we’ll discuss that within the subsequent step — this operate will return the info you need.
4. Enter the desk array of the spreadsheet the place your required knowledge is positioned.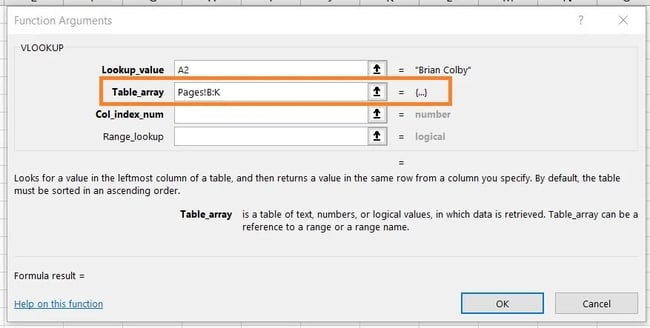
Subsequent to the “desk array” subject, enter the vary of cells you need to go looking and the sheet the place these cells are positioned, utilizing the format proven within the screenshot above. The entry above means the info we’re on the lookout for is in a spreadsheet titled “Pages” and might be discovered wherever between column B and column Ok.
The sheet the place your knowledge is positioned have to be inside your present Excel file. This implies your knowledge can both be in a distinct desk of cells someplace in your present spreadsheet, or in a distinct spreadsheet linked on the backside of your workbook, as proven beneath.
For instance, in case your knowledge is positioned in “Sheet2” between cells C7 and L18, your desk array entry will probably be “Sheet2!C7:L18.”
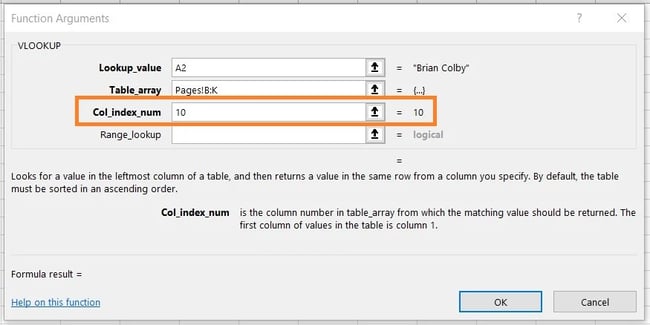
5. Enter the column variety of the info you need Excel to return.
Beneath the desk array subject, you may enter the “column index quantity” of the desk array you are looking out by means of. For instance, for those who’re specializing in columns B by means of Ok (notated “B:Ok” when entered within the “desk array” subject), however the particular values you need are in column Ok, you may enter “10” within the “column index quantity” subject, since column Ok is the tenth column from the left.
6. Enter your vary lookup to search out a precise or approximate match of your lookup worth.
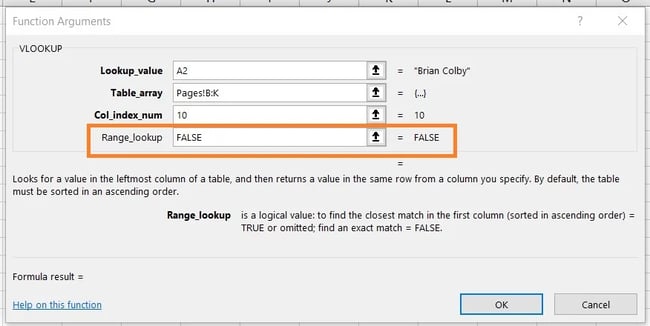
In conditions like ours, which issues month-to-month income, you need to discover actual matches from the desk you are looking out by means of. To do that, enter “FALSE” within the “vary lookup” subject. This tells Excel you need to discover solely the precise income related to every gross sales contact.
To reply your burning query: Sure, you possibly can enable Excel to search for an approximate match as a substitute of a precise match. To take action, merely enter TRUE as a substitute of FALSE within the fourth subject proven above.
When VLOOKUP is ready for an approximate match, it is on the lookout for knowledge that almost all carefully resembles your lookup worth, somewhat than knowledge that’s equivalent to that worth. In case you’re wanting up knowledge related to a listing of web site hyperlinks, for instance, and a few of your hyperlinks have “https://” initially, it would behoove you to search out an approximate match simply in case there are hyperlinks that do not need this “https://” tag. This fashion, the remainder of the hyperlink can match with out this preliminary textual content tag inflicting your VLOOKUP formulation to return an error if Excel cannot discover it.
7. Click on ‘Achieved’ (or ‘Enter’) and fill your new column.
With a view to formally deliver within the values you need into your new column from Step 1, click on “Achieved” (or “Enter,” relying in your model of Excel) after filling the “vary lookup” subject. This can populate your first cell. You would possibly take this chance to look within the different spreadsheet to ensure this was the right worth.
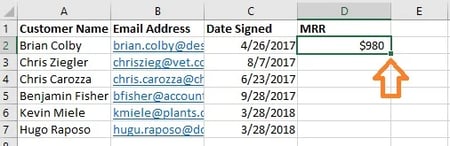
In that case, populate the remainder of the brand new column with every subsequent worth by clicking the primary crammed cell, then clicking the tiny sq. that seems on the bottom-right nook of this cell. Achieved! All of your values ought to seem.
VLOOKUP Not Working?
VLOOKUP Tutorial
Bought caught after attempting to conduct your personal VLOOKUP with the steps above? Try this useful tutorial from Microsoft has a useful tutorial that may stroll you thru correctly utilizing the operate.
In case you’ve adopted the above steps and your VLOOKUP continues to be not working, it can both be a difficulty along with your:
- Syntax (i.e. how you have structured the formulation)
- Values (i.e. whether or not the info it is wanting up is nice and formatted appropriately)
Troubleshooting VLOOKUP Syntax
Begin with wanting on the VLOOKUP formulation that you’ve got written within the designated cell.
- Is it referring to the suitable lookup worth for its key identifier?
- Does it specify the right desk array vary for the values it must retrieve
- Does it specify the right sheet for the vary?
- Is that sheet spelled appropriately?
- Is it utilizing the right syntax to consult with the sheet? (e.g. Pages!B:Ok or ‘Sheet 1’!B:Ok)
- Has the right column quantity been specified? (e.g. A is 1, B is 2, and so forth)
- Is True or False the right route for the way your sheet is ready up?
Troubleshooting VLOOKUP Values
If the syntax will not be the issue, how you might have a difficulty with the values you are attempting to obtain themselves. This typically manifests as an #N/A error the place the VLOOKUP can’t discover a referenced worth.
- Are the values formatted vertically and from proper to left?
- Do the values match the way you consult with them?
For instance, for those who’re wanting up URL knowledge, every URL have to be a row with its corresponding knowledge to the left of it in the identical row. If in case you have the URLs as column headers with the info transferring vertically, the VLOOKUP won’t work.
Retaining with this instance, the URLs should match in format in each sheets. If in case you have one sheet together with the “https://” within the worth whereas the opposite sheet omits the “https://”, the VLOOKUP will be unable to match the values.
VLOOKUPs as a Highly effective Advertising and marketing Instrument
Entrepreneurs have to investigate knowledge from a wide range of sources to get an entire image of lead era (and extra). Microsoft Excel is the proper instrument to do that precisely and at scale, particularly with the VLOOKUP operate.
Editor’s observe: This publish was initially revealed in March 2019 and has been up to date for comprehensiveness.


![Learn how to Use VLOOKUP Perform in Microsoft Excel [+ Video Tutorial]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/VLOOKUP-hero.webp#keepProtocol)
![Download 10 Excel Templates for Marketers [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9ff7a4fe-5293-496c-acca-566bc6e73f42.png)
